Home
Fundamentals
Research Data Management
FAIR Data Principles
Metadata
Ontologies
Data Sharing
Data Publications
Data Management Plan
Version Control & Git
Public Data Repositories
Persistent Identifiers
Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN)
DataPLANT Implementations
Annotated Research Context
User Journey
ARC specification
ARC Commander
QuickStart
QuickStart (Experts)
Swate
QuickStart
Walk-through
Best Practices For Data Annotation
DataHUB
DataPLAN
Ontology Service Landscape
ARC Commander Manual
Setup
Git Installation
ARC Commander Installation
Windows
MacOS
Linux
ARC Commander DataHUB Access
Before we start
Central Functions
Initialize
Clone
Connect
Synchronize
Configure
Branch
ISA Metadata Functions
ISA Metadata
Investigation
Study
Assay
Update
Export
ARCitect Manual
Installation - Windows
Installation - macOS
Installation - Linux
QuickStart
QuickStart - Videos
ARCmanager Manual
What is the ARCmanager?
How to use the ARCmanager
Swate Manual
QuickStart - Videos
Annotation tables
Building blocks
Building Block Types
Adding a Building Block
Filling cells with ontology terms
Advanced Term Search
File Picker
Templates
Contribute Templates
ISA-JSON
DataHUB Manual
Overview
User Settings
Generate a Personal Access Token (PAT)
Projects Panel
ARC Panel
Forks
Working with files
ARC Settings
ARC Wiki
Groups Panel
Create a new user group
CQC Pipelines & validation
Find and use ARC validation packages
Data publications
Passing Continuous Quality Control
Submitting ARCs with ARChigator
Track publication status
Use your DOIs
Guides
ARC User Journey
Create your ARC
ARC Commander QuickStart
ARC Commander QuickStart (Experts)
ARCitect QuickStart
Annotate Data in your ARC
Annotation Principles
ISA File Types
Best Practices For Data Annotation
Swate QuickStart
Swate Walk-through
Share your ARC
Register at the DataHUB
DataPLANT account
Invite collaborators to your ARC
Sharing ARCs via the DataHUB
Work with your ARC
Using ARCs with Galaxy
Computational Workflows
CWL Introduction
CWL runner installation
CWL Examples
CWL Metadata
Recommended ARC practices
Syncing recommendation
Keep files from syncing to the DataHUB
Working with large data files
Adding external data to the ARC
ARCs in Enabling Platforms
Publication to ARC
Troubleshooting
Git Troubleshooting
Contribute
Swate Templates
Knowledge Base
Teaching Materials
Events 2023
Nov: CEPLAS PhD Module
Oct: CSCS CEPLAS Start Your ARC
Sept: MibiNet CEPLAS Start Your ARC
July: RPTU Summer School on RDM
July: Data Steward Circle
May: CEPLAS Start Your ARC Series
Start Your ARC Series - Videos
Events 2024
TRR175 Becoming FAIR
CEPLAS ARC Trainings – Spring 2024
MibiNet CEPLAS DataPLANT Tool-Workshops
TRR175 Tutzing Retreat
Frequently Asked Questions
last updated at 2024-01-23
About this guide
In this guide we introduce how to access ARCs from Galaxy. To access the data of an ARC, you must first provide a DataHUB access token in Galaxy, which is used to authenticate Galaxy to DataHUB. To create a new token and add it to Galaxy, you can proceed as described below.
UserAdvanced
ModeTutorial
Before we can start
☑️ You have created an ARC before using the ARC Commander or ARCitect
☑️ You have a DataPLANT account
Create an access token in DataHUB
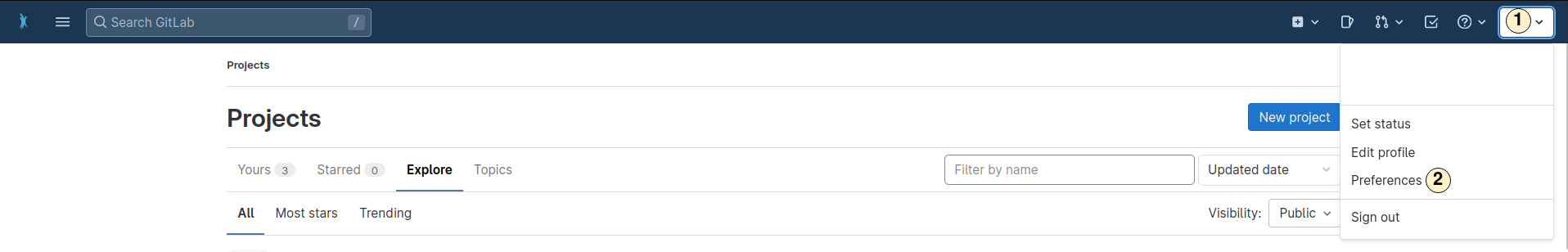
- Open the dropdown menu for your personal settings.
- Open the "Preferences" menu.
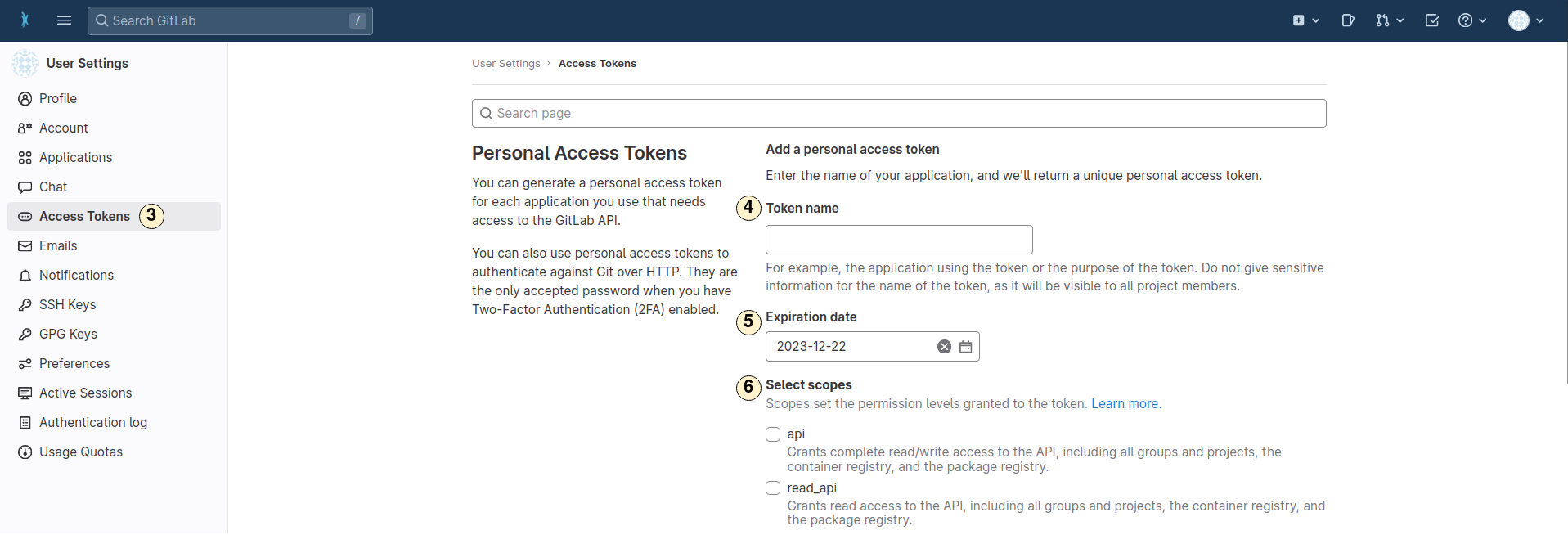
- Change to tab "Access Tokens".
- Choose a name for the new token.
- Set a expiration date.
- Select the authorization scope.
💡 Only the scopes "api" (for write access) and "read_api" (for read access) are relevant for ARCfs.
Important: After you crated the token, you can copy and view it. After you leave the
site, you will not be able to do so again.
Add the token to Galaxy

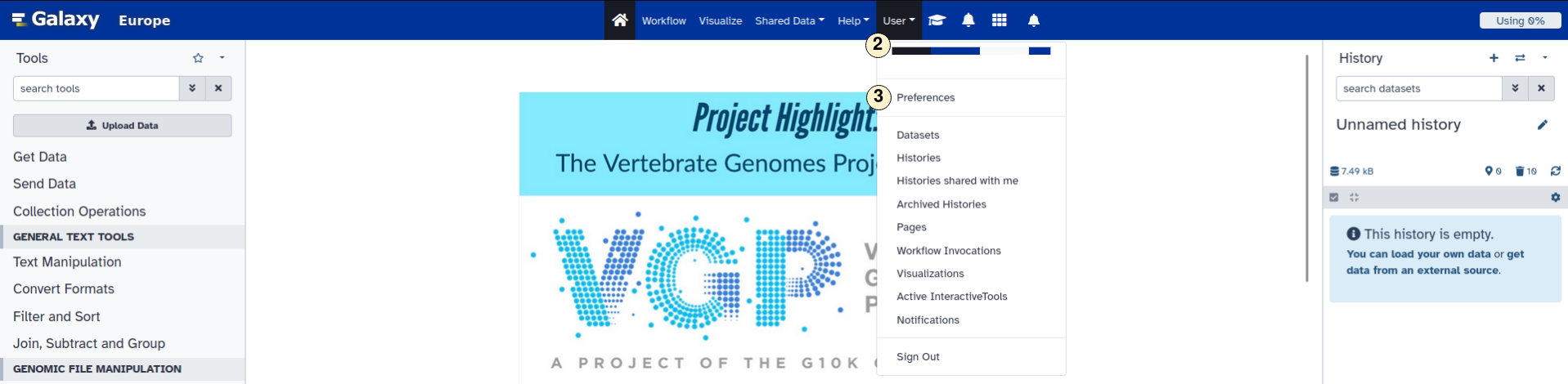

- Visit usegalaxy.eu and log in or create an account. It is possible to log in using your DataPlant account.
- Open the "User" drop down menu and
- select "Preferences".
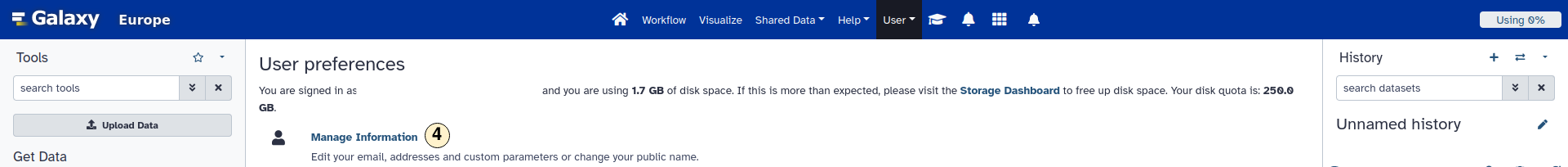
- In the user preference settings, select "Manage Information".
- Copy your token into the "API read access token" field. This filed is located at the bottom of the "User preferences" menu. Click "Save" to adopt your changes.
💡 Despite the name "API read access token", tokens with write access rights (like those with the scope "api") will also work or, respectively, are required.
Data import
With the token available to Galaxy, you are now able to import data. You can do this as described below.

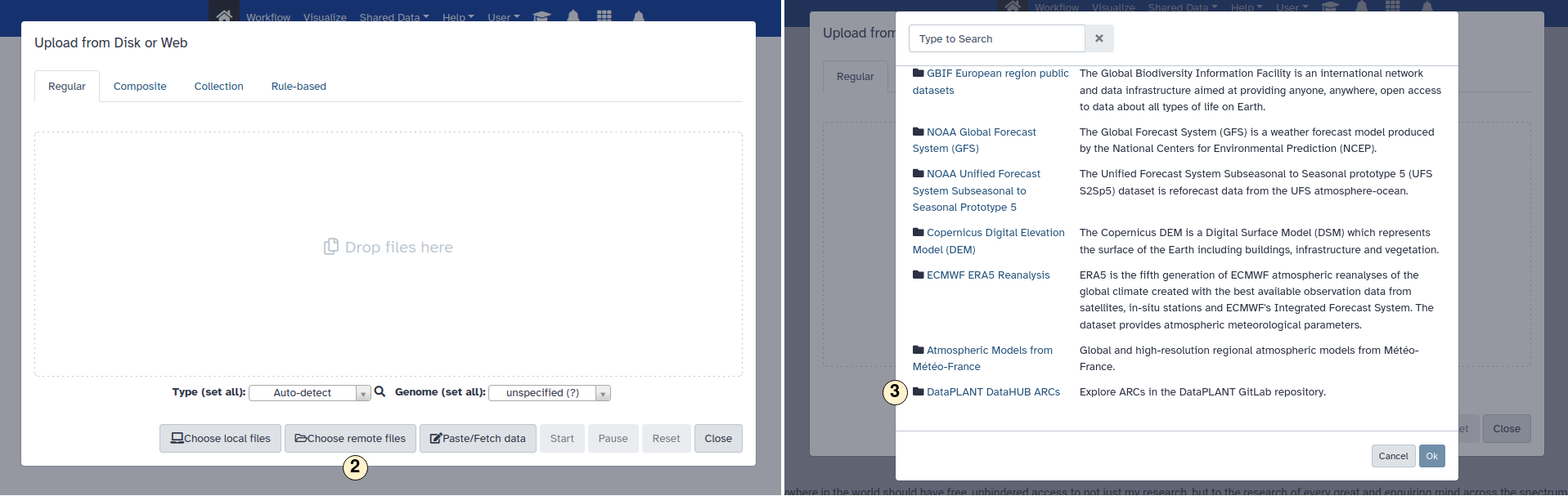
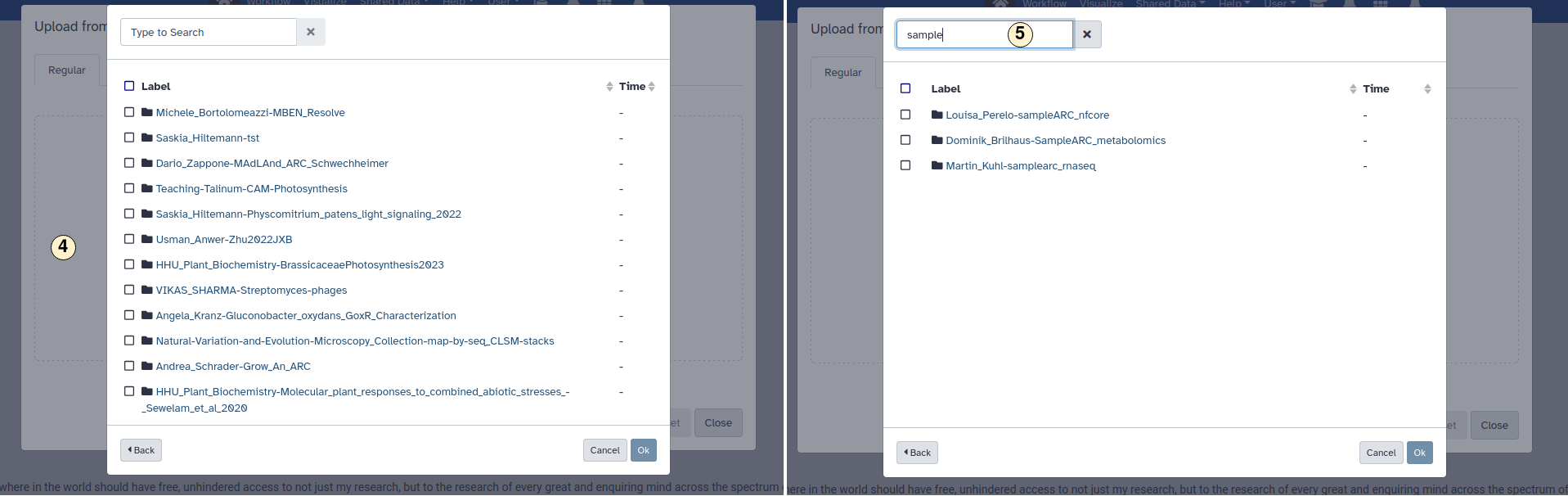
- Click on the "Upload Data".
- Pick "Choose remote files".
- Scroll down and select "DataPLANT DataHub ARRCs".
- Explore ARCs or
- search for a specific one.
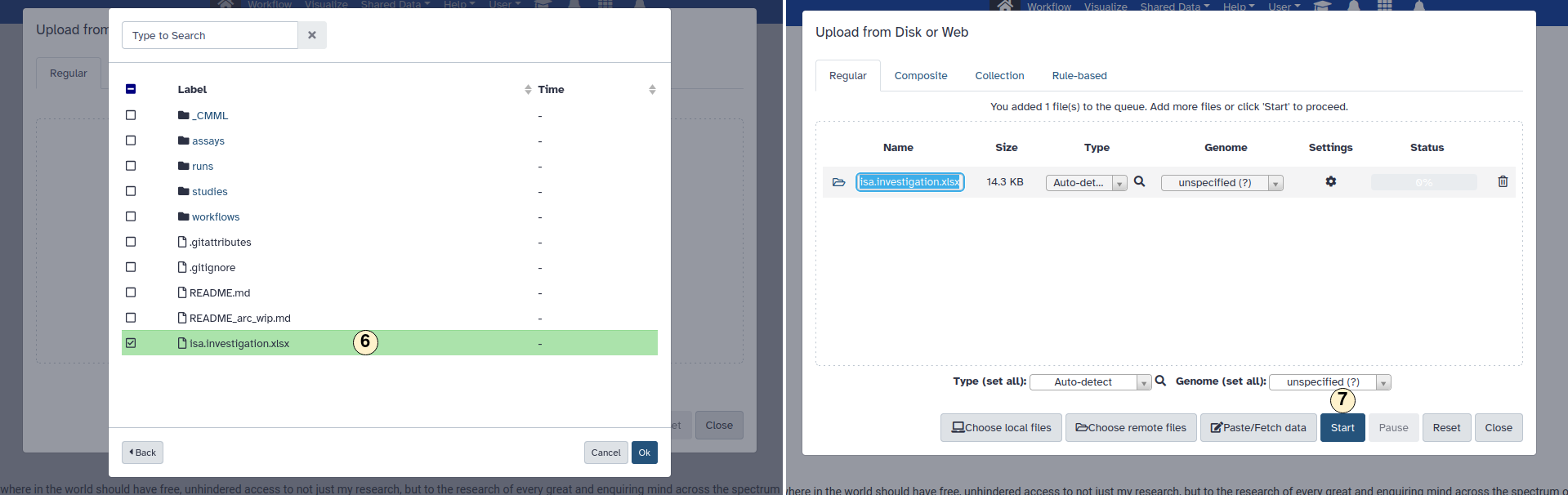
- Inside an ARC, choose the file you want to import to Galaxy. Confirm with "Ok".
- Click start to begin the import process to Galaxy. This may take some time, depending
on the workload on the Galaxy server and the size of your file.
Data export
It is also possible to export datasets back to an ARC. You can do this as described below.
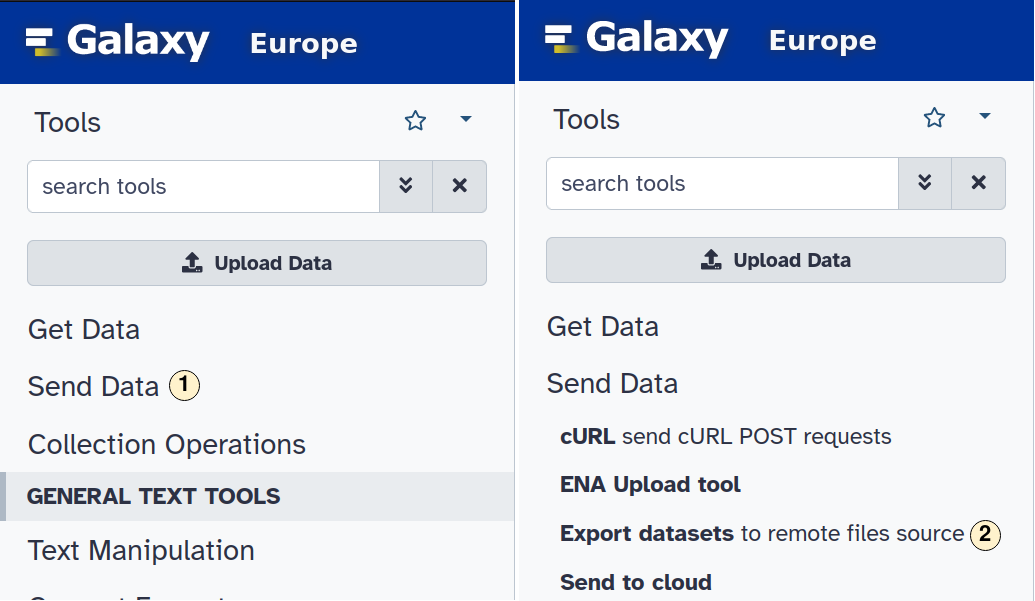
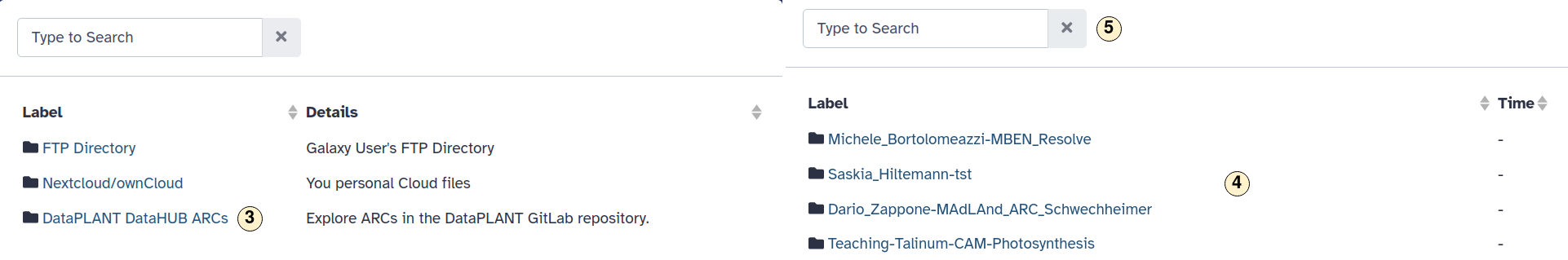
- On the left sidebar, open the menu "Send Data".
- Select "Export datasets" to remote files source.
- In the opening menu, select "DataPLANT DataHUB ARCs".
- Select or
- search for an ARC.
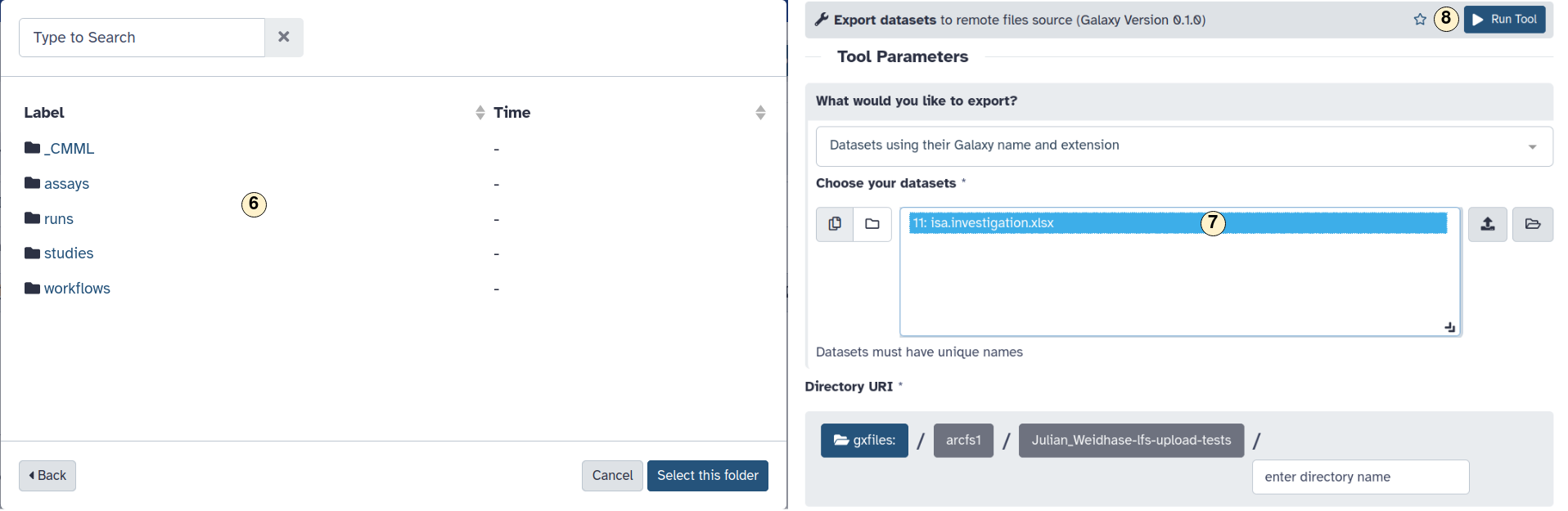
- Chose a directory inside an ARC where your dataset should be stored.
- Choose the dataset you want to export,
- Clock on "Run Tool" to start the export process. This may take some time, depending
on the workload on the Galaxy server and the size of your file.
DataPLANT Support
Besides these technical solutions, DataPLANT supports you with community-engaged data stewardship. For further assistance, feel free to reach out via our
helpdesk
or by contacting us
directly
.












