Passing Continuous Quality Control
last updated at 2023-09-07Note: All CQC pipelines are opt-in starting from July 10, 2024. If you used the DataHUB publication service before, head here to learn how to opt-in.
Continuous Quality Control (CQC) is a process that ensures the quality of the metadata of an ARC meets certain standards.
Read more about the general CQC process here.
in short the CQC pipeline is performed on each commit to an ARC, and the results of each step (e.g., validation against a user-selected validation package) are displayed on the ARC homepage:
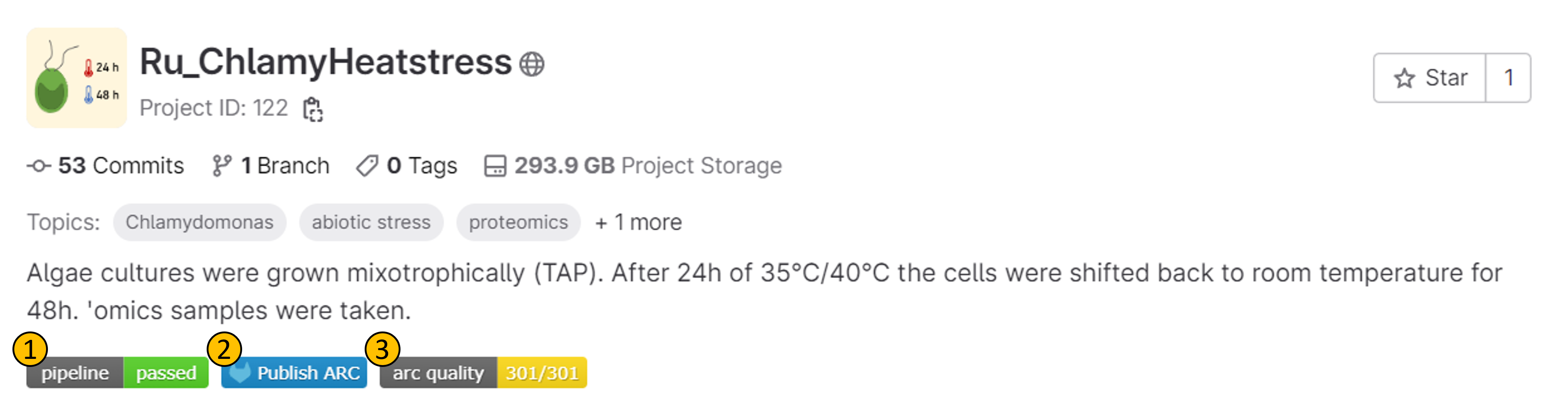
- (1): The pipeline badge indicates wether all steps of CQC have passed, or if there are any failures.
- (2): The publish button is used to submit the ARC to the ARChive via ARChigator. Note that ARCs that fail CQC are not eligible for publication.
- (3): The arc quality badge indicates the overall metadata quality of the ARC. This is calculated based on the results of the CQC pipeline, and signifies how many of the performed tests have passed. The badge is color-coded, and the color indicates the quality of the ARC.
For more details, you can click on the pipeline badge (1), and investigate the steps of the CQC pipeline details:
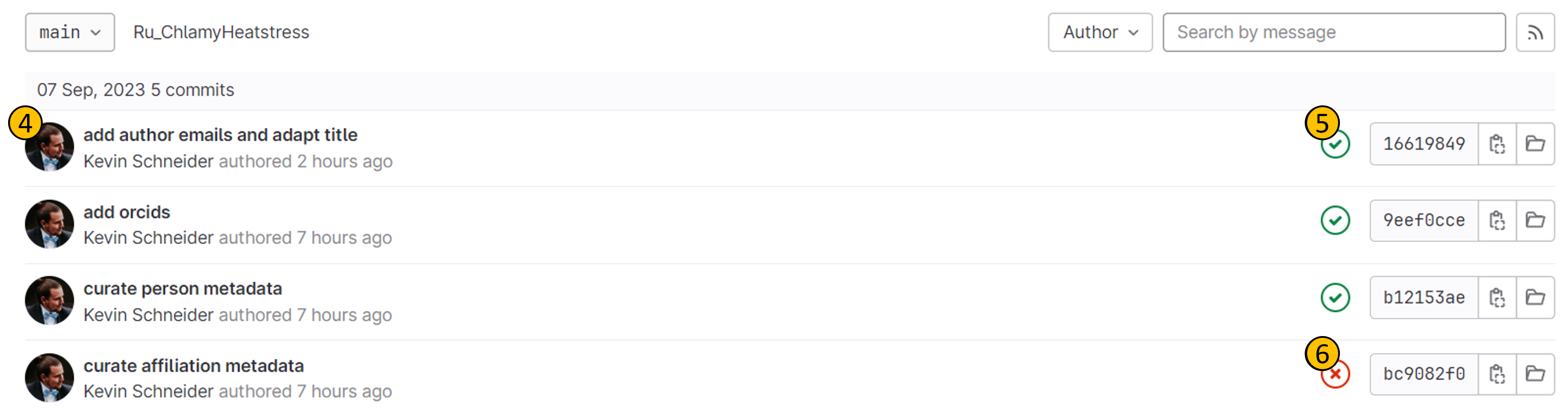
- (4): List of commits, with the most recent commit on top.
- (5): Pipeline result: If the pipeline passed, it shows a green checkmark.
- (6): Pipeline result: If the pipeline failed, it shows a red cross.
Click on a pipeline result (e.g., (4)) of a commit of choice to open the CQC pipeline details for that commit.
On the next page, you can see the details of the CQC pipeline for the selected commit:
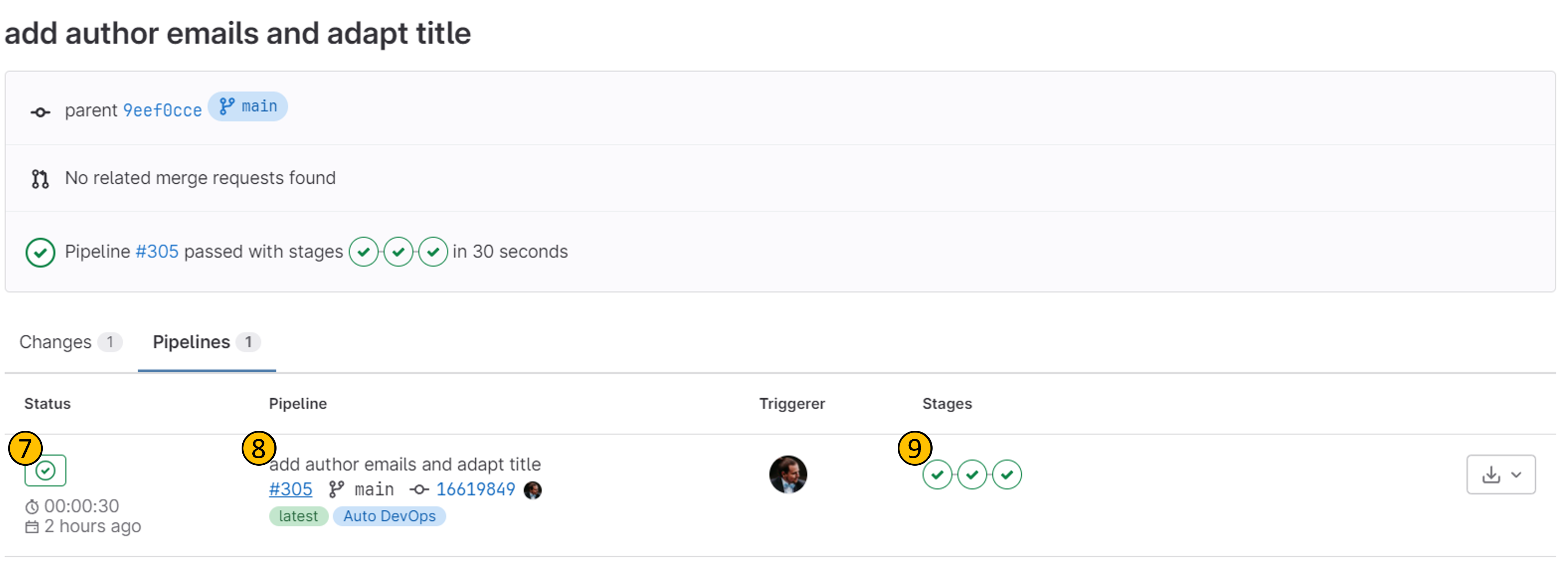
- (7): overall pipeline result
- (8): associated commit information
- (9): pipeline step results
Clicking on (7) will open the CQC pipeline, where each step can be viewed in detail:
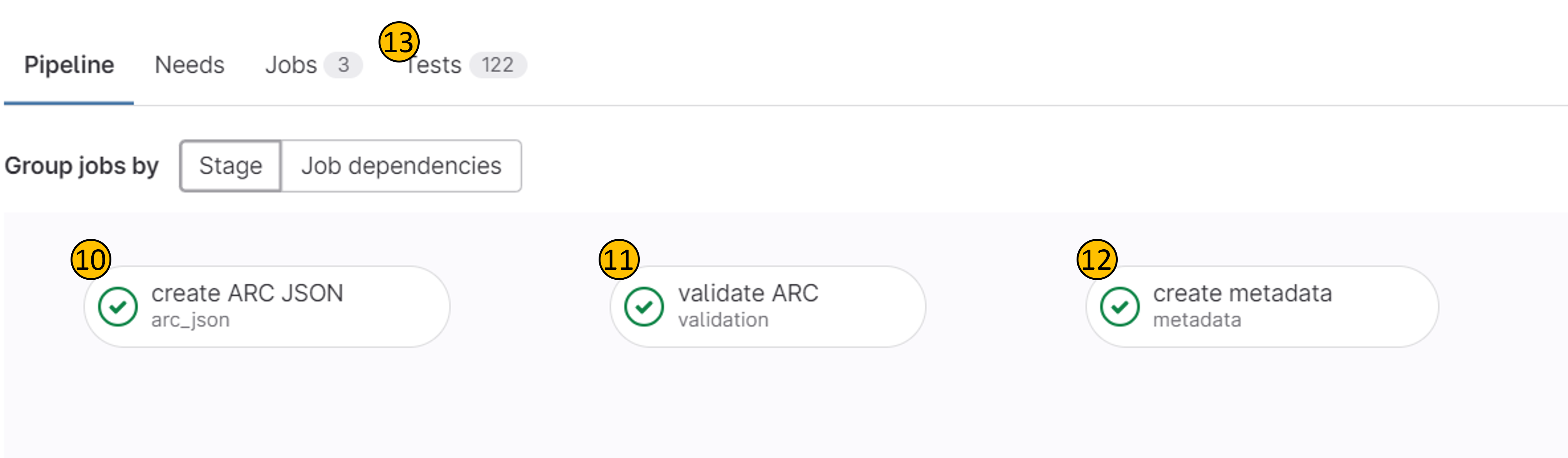
- (10) CQC step 1: a machine-readable representation (JSON) of the ARC metadata is created and linked with the commit, which makes it discoverable for search tools.
- (11) CQC step 2: ARC metadata is subjected to a set of quality checks, e.g., if ORCIDs associated with persons are valid or if each author has a contact email.
- (12) CQC step 3: The ARC metadata is converted to a metadata record, which is used by subsequent tools to trigger the data publication and associated creation of a DOI via DataCite for that record.
- (13): Test tab shows the results of each individual test performed in CQC step 2 (11)
To start the publication process, first make sure to install the invenio validation package. Clicking on the publish button (2) on the ARC homepage will start the publication process. Refer to the ARChigator guide for more information on the publication process.
There are multiple issues that can lead to a failed CQC pipeline:
CQC step 1 (10), should never fail, as it usually creates a json file even when there is no ARC in the repository. If this step fails, please contact the DataHUB support team, as there is something fundamentally wrong with your repository.
CQC step 2 (11), is the most common step to fail. This step contains a set of critical quality checks that MUST pass in order for the ARC to be eligible for publication, and a set of non-critical checks that signify metadata quality. Only failed critical tests lead to a failed CQC pipeline. If this happens, investigate the failed tests in the Test tab (13), and fix the issues based on the information displayed there. An example could for example be a person not having a First name in your investigation metadata. Commit your changes and check wether the tests pass.
As CQC step 3 (12) is only performed after the ARC has passed all critical tests (10), it is very unlikely that this step fails. If it does, please contact the DataHUB support team.